Charter schools and home schooling are experiencing major growth. Meanwhile, there were no significant differences between students in charter schools and traditional public schools in average reading and mathematics scores on national tests in 2017.
Those are two of the key findings in the U.S. Department of Education’s (USDOE) latest report, “School Choice in the United States,” which updates the national changing landscape for school choice with changes in enrollment data, academic performance updates, and parental satisfaction surveys. Nationally, charter public schools and district schools increased enrollment while private schools declined.
Overall, there were around 57.8 million K-12 students in the United States, up from 53.8 million in 1999. Based on figures from the USDOE, the market share of district schools fell from 87 percent of all students in 1999 to 81.8 percent of students by 2016.
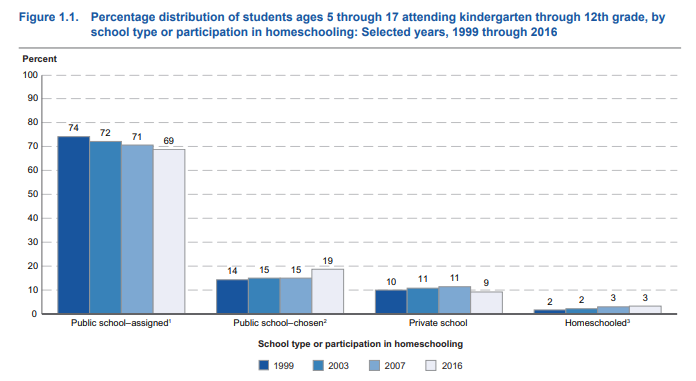
From 1999 to 2016 the share of students attending their assigned neighborhood public schools dropped from 74 percent to 69 percent. Public school choice option, including charter schools, magnet schools and open enrollment programs, grew from 14 percent of the student body in 1999 to 19 percent. Charter schools alone grew a staggering 571 percent from 2000 to 2016, enrolling over 3 million students by 2016.
Private school options fell from 10 percent to 9 percent, while home education grew from 2 percent to 3 percent by 2016.
Unlike most of the nation, however, Florida has seen private school enrollment bounce back. In 2000, 348,000 students enrolled in nonpublic schools, comprising 12.5 percent of the total PK-12 student body. Thanks to the help of several private school programs, including the Florida Tax Credit Scholarship, private schools in the Sunshine State continue to grow. In 2018-19, the latest data available, 380,000 students enrolled in nonpublic schools, though the market share has declined to 11.8 percent of Florida’s total PK-12 student population.
Catholic schools remain the top choice among private school parents, enrolling more than 2 million students in 2016, more than double any other denomination.
District schools enrolled 94 percent of all public school students, with charters enrolling the other 6 percent. District schools were more likely to enroll white students, and less likely to enroll black or Hispanic students, than charters. According to the USDOE, 57 percent of public schools were 50 percent or more white, while just 33 percent of charters were. Charters were more likely to be 50 percent or higher black or Hispanic, however.
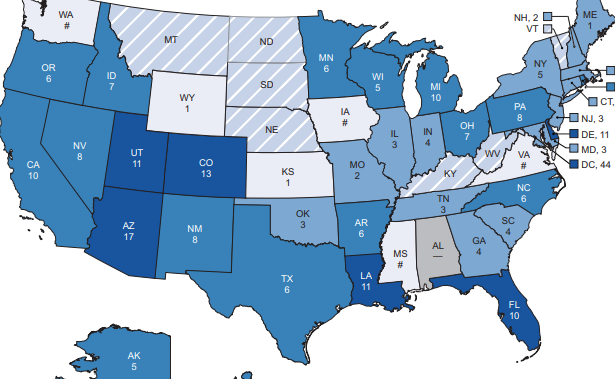
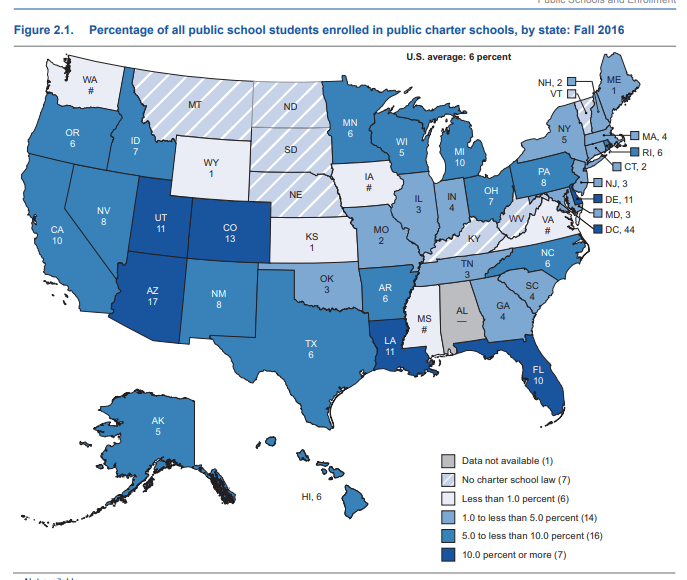
Enrollment in charter options varies greatly among states, though one important pattern emerges just in time for the Democratic presidential primaries: Important swing states Florida, Arizona and Michigan have large charter school populations.
Meanwhile, the USDOE reports “no measurable difference” between the average district students and charter school students on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) exams in reading in math in 2017.
Charter school students, including black, Hispanic and free and reduced-price lunch students, saw higher raw NAEP scores in fourth-grade reading than in traditional public schools, and were no different on eighth-grade reading. White, black and Hispanic students attending charters also saw higher raw scores on eighth-grade math, and were no different on fourth-grade math.
According to the report, 1.7 million students attended a home school setting in 2016. Home school students were more likely to live in a rural setting or small town than be urban or suburban. Homeschooling was also more common in the South and West than in the Northeast.
Home school parents had various reasons for choosing the option, according to the USDOE. About 34 percent of home education parents chose home schooling over public schools due to concerns about a school’s environment such as safety, drugs or negative peer pressure. Seventeen percent were dissatisfied with instruction, and 16 percent wanted to provide religious instruction.
Choice also played a significant role in parental satisfaction. Sixty percent of parents choosing a public school option were satisfied with the school, compared to 54 percent of parents with students at assigned public schools. Seventy-seven percent of parents enrolling children in private schools reported being satisfied with the school. A similar pattern emerges regarding satisfaction for academic standards, school discipline and regarding interaction between staff and parents.


